Contact Info
-
45, Sector 7A Faridabad, 121006, IN
- thebonejointclinic@gmail.com
- +91 82872 71544

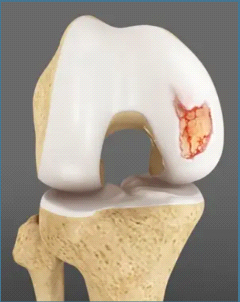
Cartilage is soft, white and lubricating cushion at the bone end that make the knee gliding and function well.
It can be damaged due to trauma, pivot injury and with age(overuse), it can also come out along with bone piece known as osteochondral fragment (OCD)
Symptoms : In short term, it can cause pain, swelling, difficulty in weight bearing on affected knee and locking symptoms but in long term, it can cause osteoarthritis of knee that can land up with knee replacement.
After checking your symptoms, we will examine your knee for cause of tenderness, stiffness, swelling and any difficulty in walking. We will advise xray to confirm diagnosis of arthritis and MRI of knee to see damage in soft tissues (cartilage, tendon and ligaments) of knee.
In short term, it can cause pain, swelling, difficulty in weight bearing on affected knee and locking symptoms but in long term, it can cause osteoarthritis of knee that can land up with knee replacement.
If we manage it at early stage that symptoms subsided early and can achieve knee function restoration early. Osteoarthritis will be delayed
Knee chondroplasty
Used for minor cartilage problems, chondroplasty involves removing loose flaps of cartilage (which can cause a sensation of catching or pain in the joint) or fragments of tissue, as well as smoothing damaged areas. It’s usually carried out using keyhole surgery (Arthroscopy). Recovery is faster than for traditional open surgery and in most cases, patients can drive again one to three weeks after the operation.
Microfracture
It can be used to treat more serious knee cartilage injuries and helps with the formation of new joint surface cartilage. The damaged cartilage is debrided and the bone is then punctured with a specially designed tool to create a number of holes that causes the bone to bleed. This in turn causes the cartilage to heal, while forming new tissue.
To make this surgery successful, you’ll be advised to use crutches for six weeks after surgery before gradually returning to your usual activities.
Osteochondral fragment fixation
when the articulating cartilage (chondro) and part of the underlying bone (osteo) breaks off of the bone itself and become a fragment.
If the fragment stays in place it is considered stable, but if it breaks loose then it is labeled as unstable. Unstable fractures can move around in the joint and cause pain as well as other symptoms. These fragments, or loose bodies, can vary in size.
This loose fragment should be fixed in first 2 weeks to maintain the viability. It can be fixed with Herbert screws, bio-screws, bio-wires and suture anchors
Nanofracture (AMIC)
Autologous matrix-induced chondrogenesis, or AMIC is a new one-stage treatment used to repair cartilage. It combines microfracture surgery with the use of collagen to help repair damage and regain full mobility of the joint.
It’s an arthroscopic surgery, it involves a tiny amount of cartilage being taken from your knee and then implanted into a matrix made of collagen which is immediately replaced into the knee joint. Afterwards, you’ll be given a personalized physiotherapy rehabilitation program to ensure the fastest recovery and best possible results.
To make this surgery successful, you’ll be advised to use crutches for six weeks after surgery before gradually returning to your usual activities.
Knee cartilage transplantation (MACI)
This two-stage technique, known as matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation (MACI) is carried out by arthroscopic surgery. During the first procedure, a small amount of cartilage is taken from your knee and then grown in a laboratory to produce more cartilage that is attached to a matrix made of collagen. During the second procedure, the cartilage cells are implanted in the joint. Afterwards, you’ll be given a personalised physiotherapy rehabilitation programme to ensure the fastest recovery and best possible results.
To make this surgery successful, you’ll be advised to use crutches for six weeks after surgery before gradually returning to your usual activities.
OATS surgery
Osteoarticular transfer system, or OATS, usually involves arthroscopic surgery and possibly a small open incision during which cartilage is removed and replaced with healthy cartilage taken from another non weight bearing area of the joint (autograft transplantation). It can be performed alongside other procedures including ACL surgery. Afterwards, you’ll be given a personalised rehabilitation programme to ensure the fastest recovery and best possible results.
To make this surgery successful, you’ll be advised to use crutches for six weeks after surgery before gradually returning to your usual activities.
Osteochodral allograft transplantation
Healthy tissue from a donor is transplanted to the injured site. This can be performed alongside other procedures including ACL surgery. Afterwards, you’ll be given a personalised rehabilitation programme to ensure the fastest recovery and best possible results.
Patients treated with Cartilage repair, all demonstrated statistically significant improvements in functional outcome scores with radiographic evidence of healing at minimum of 2-year follow-up.