Contact Info
-
45, Sector 7A Faridabad, 121006, IN
- thebonejointclinic@gmail.com
- +91 82872 71544

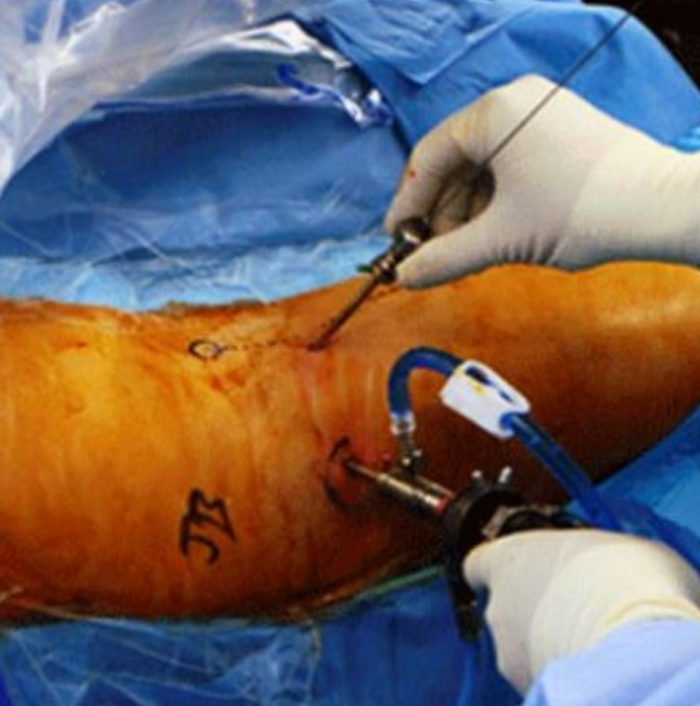
Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgery used to treat problems in your hip. Surgeon will make a few small incisions (cuts) in the skin of hip and then insert a special tool called an arthroscope into your hip joint. The arthroscope includes a camera and a light that lets you identify and repair damage inside your hip. They’ll also insert any other small instrument, they need to repair damage to hip bone and soft tissue.
Hip arthroscopy is generally recommended for younger patients with hip pain who do not require a hip replacement. The cause of their pain is usually related to sports injuries to the hip, overuse injuries or abnormalities in the shape of the bones that make up the hip joint. Hip arthroscopy is usually not an option for those with osteoarthritis.
Hip arthroscopy may be an option if you’ve been diagnosed with or suspicion of:
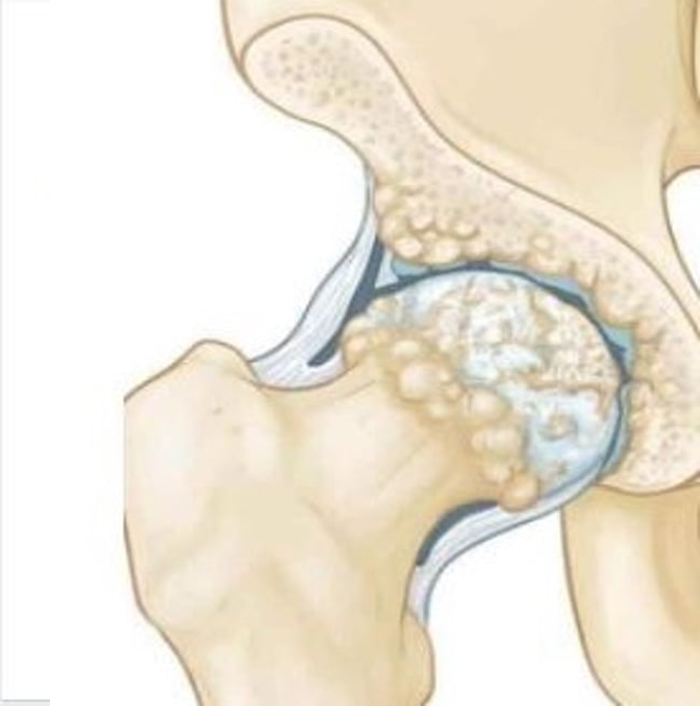
Hip impingement: pinching between the bones of the hip joint due to irregular bone shape. Arthroscopy can be used to reshape the bones.
Hip labral tear: a tear in the ring of cartilage that rims the hip socket. Arthroscopy can be used to clean out damaged labrum, repair the tear and address underlying causes such as hip impingement.
Loose fragments of cartilage in the joint after an injury: Arthroscopy can help remove any debris from the hip joint.
Bone spurs (osteophytes): bony bumps that form on the ends of the bones and can prevent the joint from gliding smoothly. Arthroscopy can be used to shave off the spurs and restore the shape of the joint.
Synovitis: inflammation of the joint lining. Arthroscopy can be used to remove the inflamed tissue as well as diagnose and treat the underlying causes.
Because these conditions may contribute to the development of hip arthritis over time, treating them with hip arthroscopy can help delay or slow down arthritis, thus postponing the need for hip replacement.
Benefits
What are the advantages of hip arthroscopy?
Hip arthroscopy is much less invasive than other types of surgery.
A faster recovery time.
Less pain after the surgery.
Minimal blood loss and scarring.
Lower risk for complications compared to more invasive surgery techniques.
Risks
Allergic reaction to anesthesia.
Blood clots, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Damage to surrounding tissue or nerves.
Excessive bleeding or swelling.
Infections.
Numbness or tingling in your groin, thigh or foot.
A need for further surgery if your underlying issues don’t improve.
Most people recover from a hip arthroscopy in around six weeks. Exact time to heal fully will depend on type of surgery done.
You’ll need crutches for 1-2 weeks after surgery. After that, you should be able to walk and put more weight on your hip.
You will also need physical therapy. This could last anywhere from a few weeks to a few months after your surgery. You should be able to return to heavy exercise and/or sports in around 12 weeks.


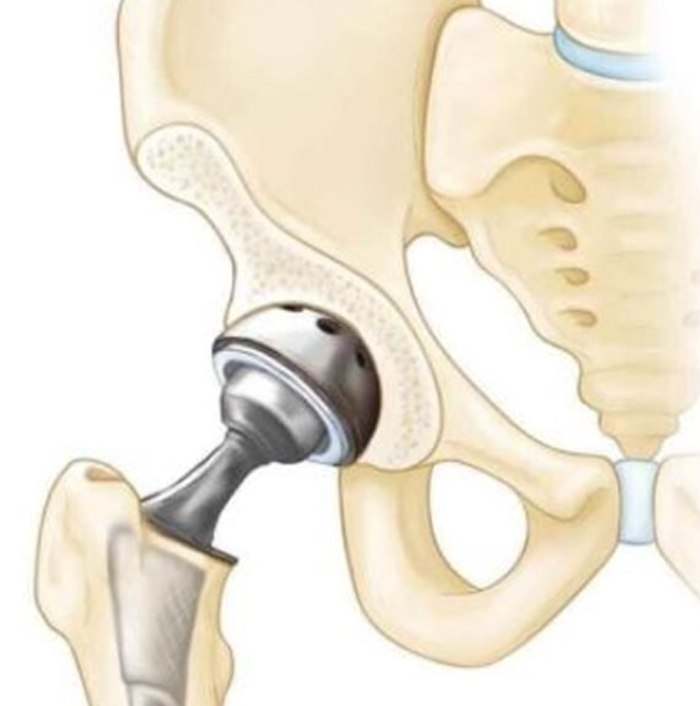
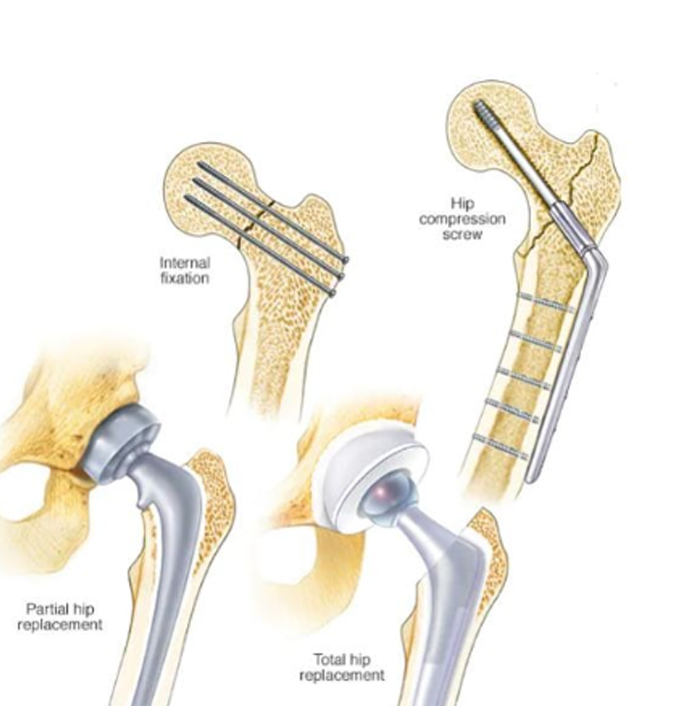
Arthroplasty (Joint Replacement) for hip arthritis
Arthroscopy (Durbin se operation) for sports injury and related issues
There are also various health and motivation tips available to help you along the way.